|
Size: 2373
Comment:
|
Size: 4577
Comment:
|
| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 7: | Line 7: |
| Put the following lines in the head of your document, i.e. between `\documentclass{xxx}` and `\begin{document}` | Put the following lines in the head of your document, i.e. between `\documentclass{xxx}` and `\begin{document}`. The package `mathtools` is an extension of `amsmath`, and may be of interest independently of optimization problems. |
| Line 9: | Line 9: |
| \usepackage{mathtools} | |
| Line 17: | Line 18: |
| {{attachment:optim1.png|text describing image}} |
This is a simple optimization. Note that the equation number is put at the expression to be minimized, using the command `\tagthis`. For other numbering patterns, see below. Note also that the first column, with 'minimize' and 'subject to', is right aligned, and the second column is left aligned. Other alignments are possible, but this is the simplest and most estetic in my opinion.<<BR>> {{attachment:optim1.png}} |
| Line 26: | Line 27: |
| This is a more complex optimization. Note that the expressions under 'minimize' is in fact wider than the word 'minimize'. This is acheived through the command `\clap`, which typesets its arguments centered and with an apparent width of 0pt. It is therefore up to yourself to allow a reasonable extra width. This command is available through the package 'mathtools'. Note also that the `\tagthis` command is on the second line, because that line is a continuation line.<<BR>> | |
| Line 27: | Line 29: |
| {{{ | {{{latex |
| Line 29: | Line 31: |
| \optmin{\begin{matrix}\Delta\bm{\theta}_{\mathrm{SOI}},\Delta \theta_{\mathrm{HP}},\\ \Delta \theta_{\mathrm{LP}},\Delta\theta_{\mathrm{Hot}}\end{matrix}} &\sum_{k=1}^{H_p}\biggl(\omega_1||r_{\theta_{50}}(k)-\bm{\theta}_{50}(k)||^2_2 + \omega_2 ||r_{\tau}(k)-\bm{\tau}(k)||^2_2 \\[-7mm] & \hphantom{\sum} \quad + \omega_3 \theta_{\mathrm{HP}}(k)^2 + \omega_4 \theta_{\mathrm{LP}}(k)^2\biggl) + \cdots \tagthis\\ \subject & l_b \leq \begin{pmatrix} \bm{\theta}_{\mathrm{SOI}} \\ \theta_{\mathrm{Hot}} \\ \theta_{\mathrm{HP}} \\ \theta_{\mathrm{LP}} \end{pmatrix} \leq u_b \\ & \text{other conditions} |
\optmin{\begin{matrix}\Delta\theta_{\mathrm{SOI}},\Delta \theta_{\mathrm{HP}},\\ \Delta \theta_{\mathrm{LP}},\Delta\theta_{\mathrm{Hot}}\end{matrix}} &\sum_{k=1}^{H_p}\biggl(\omega_1||r_{\theta_{50}}(k)-\theta_{50}(k)||^2_2 + \omega_2 ||r_{\tau}(k)-\tau(k)||^2_2 \\[-7mm] &\hphantom{\sum} \quad + \omega_3 \theta_{\mathrm{HP}}(k)^2 + \omega_4 \theta_{\mathrm{LP}}(k)^2\biggl) + \cdots \tagthis\\ \subject & l_b \leq \begin{pmatrix} \theta_{\mathrm{SOI}} \\ \theta_{\mathrm{Hot}} \\ \theta_{\mathrm{HP}} \\ \theta_{\mathrm{LP}} \end{pmatrix} \leq u_b \\ & \text{other conditions} |
| Line 40: | Line 42: |
| }}} | latex}}} This is another fairly complex optimization, that uses the environment `alignat` to enable two columns for description of the conditions. Note that the main expression extends above the second column of the conditions. The way to achieve this is to use `\mathrlap{}` so that the apparent width of the expression is 0pt. The default distance between the columns is quite small, so a `\quad` is inserted after the longest entry in the first column.<<BR>> |
| Line 44: | Line 48: |
| \optmin{\mathbf{u}_1 , \dots , \mathbf{u}_{H_p}} & \sum_{k=1}^{H_p} J_{m_f}(k) + J_{p_{\text{IMEP}}}(k) + J_{\Delta u}(k) \hspace*{-40mm} &&\tagthis\\ \subject & p_k \leq c_{p_{\text{max} }} &&\forall\theta,\;k = 1, \ldots, H_p \\ & dp/d\theta_k \leq c_{dp_{\text{max}}} &\quad& \forall\theta,\; k = 1, \ldots, H_p \\ & \text{NO}_{x}(k) \leq c_{\text{NO}_x} && k = 1, \ldots, H_p \\ & T_{\text{ex}}(k) \geq c_{T_{\text{ex} }} &&k = 1, \ldots, H_p^{T_{\text{ex}}} \\ & \mathbf{u}(k) \in \mathbb{U} &&k = 1, \ldots, H_p. |
\optmin{\mathbf{u}_1 , \dots , \mathbf{u}_{H_p}} & \mathrlap{\sum_{k=1}^{H_p} J_{m_f}(k) + J_{p_{\text{IMEP}}}(k) + J_{\Delta u}(k)} &&\tagthis\\ \subject & p_k \leq c_{p_{\text{max} }} &\forall\theta,\;k &= 1, \ldots, H_p \\ & dp/d\theta_k \leq c_{dp_{\text{max}}}\quad & \forall\theta,\; k &= 1, \ldots, H_p \\ & \text{NO}_{x}(k) \leq c_{\text{NO}_x} & k &= 1, \ldots, H_p \\ & T_{\text{ex}}(k) \geq c_{T_{\text{ex}}} &k &= 1,\ldots,H_p^{T_{\text{ex}}} \\ & \mathbf{u}(k) \in \mathbb{U} &k &= 1, \ldots, H_p. |
| Line 53: | Line 57: |
=== Alternative numbering patterns === In the examples above, I have put the only equation number on the expression to be optimized. Other patterns are possible: One number, vertically centered.<<BR>> {{attachment:optim4.png}} {{{latex \begin{equation}\label{key} \begin{aligned} \optmin{x} &\dfrac{1}{2}x^THx + f^Tx \\ \subject & Ax \leq b \\ &A_{\text{eq}}x = b_{\text{eq}} \end{aligned} \end{equation} latex}}} All lines numbered using a subordinate numbering scheme.<<BR>> {{attachment:optim5.png}} {{{latex \begin{subequations} \begin{align} \optmin{x} &\dfrac{1}{2}x^THx + f^Tx \\ \subject & Ax \leq b \\ &A_{\text{eq}}x = b_{\text{eq}} \end{align} \end{subequations} latex}}} |
Formatting Optimization Problems
Put the following lines in the head of your document, i.e. between \documentclass{xxx} and \begin{document}. The package mathtools is an extension of amsmath, and may be of interest independently of optimization problems.
\usepackage{mathtools}
\newcommand*{\optMinMax}[2]{\underset{\vphantom{A}\displaystyle\mathclap{#1}}%
{\text{#2}}\quad}
\newcommand{\optmin}[1]{\optMinMax{#1}{minimize}}
\newcommand{\optmax}[1]{\optMinMax{#1}{maximize}}
\newcommand*{\subject}{\text{subject to}\quad}
\newcommand*{\tagthis}{\stepcounter{equation}\tag{\theequation}}This is a simple optimization. Note that the equation number is put at the expression to be minimized, using the command \tagthis. For other numbering patterns, see below. Note also that the first column, with 'minimize' and 'subject to', is right aligned, and the second column is left aligned. Other alignments are possible, but this is the simplest and most estetic in my opinion.
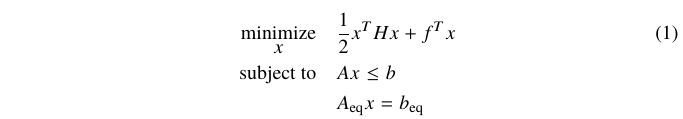
\begin{align*}\label{eq:QP}
\optmin{x} &\dfrac{1}{2}x^THx + f^Tx \tagthis \\
\subject & Ax \leq b \\
&A_{\text{eq}}x = b_{\text{eq}}
\end{align*}This is a more complex optimization. Note that the expressions under 'minimize' is in fact wider than the word 'minimize'. This is acheived through the command \clap, which typesets its arguments centered and with an apparent width of 0pt. It is therefore up to yourself to allow a reasonable extra width. This command is available through the package 'mathtools'. Note also that the \tagthis command is on the second line, because that line is a continuation line.
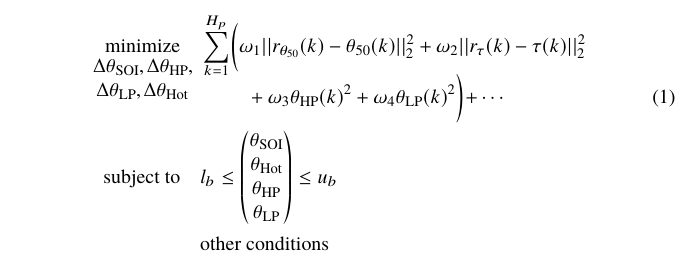
\begin{align*}\label{Eq:Ign_Opt}
\optmin{\begin{matrix}\Delta\theta_{\mathrm{SOI}},\Delta \theta_{\mathrm{HP}},\\
\Delta \theta_{\mathrm{LP}},\Delta\theta_{\mathrm{Hot}}\end{matrix}}
&\sum_{k=1}^{H_p}\biggl(\omega_1||r_{\theta_{50}}(k)-\theta_{50}(k)||^2_2
+ \omega_2 ||r_{\tau}(k)-\tau(k)||^2_2 \\[-7mm]
&\hphantom{\sum} \quad + \omega_3 \theta_{\mathrm{HP}}(k)^2
+ \omega_4 \theta_{\mathrm{LP}}(k)^2\biggl) + \cdots \tagthis\\
\subject & l_b \leq \begin{pmatrix} \theta_{\mathrm{SOI}} \\
\theta_{\mathrm{Hot}} \\ \theta_{\mathrm{HP}} \\ \theta_{\mathrm{LP}}
\end{pmatrix} \leq u_b \\
& \text{other conditions}
\end{align*}This is another fairly complex optimization, that uses the environment alignat to enable two columns for description of the conditions. Note that the main expression extends above the second column of the conditions. The way to achieve this is to use \mathrlap{} so that the apparent width of the expression is 0pt. The default distance between the columns is quite small, so a \quad is inserted after the longest entry in the first column.
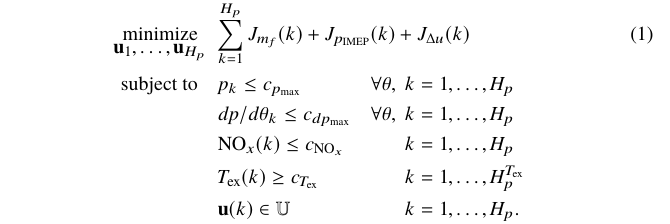
\begin{alignat*}{2}\label{Eq:opt1}
\optmin{\mathbf{u}_1 , \dots , \mathbf{u}_{H_p}}
& \mathrlap{\sum_{k=1}^{H_p} J_{m_f}(k) + J_{p_{\text{IMEP}}}(k) + J_{\Delta u}(k)} &&\tagthis\\
\subject & p_k \leq c_{p_{\text{max} }} &\forall\theta,\;k &= 1, \ldots, H_p \\
& dp/d\theta_k \leq c_{dp_{\text{max}}}\quad & \forall\theta,\; k &= 1, \ldots, H_p \\
& \text{NO}_{x}(k) \leq c_{\text{NO}_x} & k &= 1, \ldots, H_p \\
& T_{\text{ex}}(k) \geq c_{T_{\text{ex}}} &k &= 1,\ldots,H_p^{T_{\text{ex}}} \\
& \mathbf{u}(k) \in \mathbb{U} &k &= 1, \ldots, H_p.
\end{alignat*}
Alternative numbering patterns
In the examples above, I have put the only equation number on the expression to be optimized. Other patterns are possible:
One number, vertically centered.
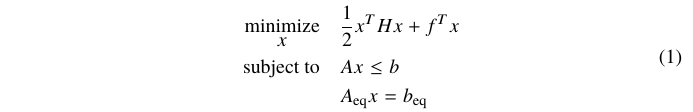
\begin{equation}\label{key}
\begin{aligned}
\optmin{x} &\dfrac{1}{2}x^THx + f^Tx \\
\subject & Ax \leq b \\
&A_{\text{eq}}x = b_{\text{eq}}
\end{aligned}
\end{equation} All lines numbered using a subordinate numbering scheme.
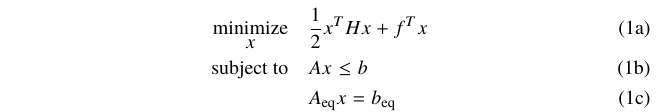
\begin{subequations}
\begin{align}
\optmin{x} &\dfrac{1}{2}x^THx + f^Tx \\
\subject & Ax \leq b \\
&A_{\text{eq}}x = b_{\text{eq}}
\end{align}
\end{subequations} 
